Hyperprolactinemia, a condition characterized by elevated levels of the hormone prolactin in the bloodstream, has the potential to significantly impact the fertility of both men and women. It is imperative for individuals with fertility concerns to comprehend the implications of hyperprolactinemia on reproductive health.
This article investigates the complexities of hyperprolactinemia and its impact on fertility, including symptoms, causes, diagnosis, treatment options, and management strategies. By shedding light on this frequently disregarded aspect of reproductive health, individuals may gain valuable insight into the challenges they may face when managing hyperprolactinemia and fertility concerns.
Definition of hyperprolactinemia
Hyperprolactinemia is a condition in which the pituitary gland produces an excessive amount of milk, regardless of whether or not the individual is suckling. This results in an increase in the production of prolactin, the hormone responsible for milk production.
Link between hyperprolactinemia and fertility
The delicate hormonal equilibrium necessary for ovulation and sperm production may be disrupted when prolactin levels are elevated. This hormonal instability has the potential to significantly disrupt your reproductive plans, potentially occurring more rapidly than you can say “prolactin who?”
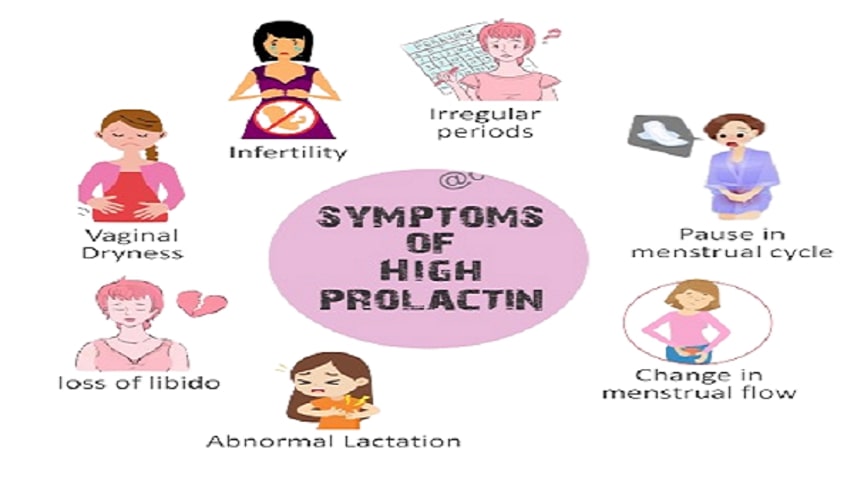
Causes and Symptoms of Hyperprolactinemia in Men and Women
Considerations for women include irregular periods, difficulties conceiving, and the production of breast milk during non-baby periods. Men may experience diminished libido, erectile dysfunction, or even breast growth. You have yet to RSVP to the hormonal celebration that your body is hosting.
The fundamental causes of hyperprolactinemia in men
The most prevalent causes of hyperprolactinemia in men are chronic renal disease, medications, pituitary tumors, and stress. Indeed, the mere act of managing one’s daily existence may induce hormonal excess.
Cabergoline 0.5mg Tablet is used to treat infertility and abnormal breast milk production (galactorrhea) caused by an excess of the natural hormone prolactin. If you’ve been sitting or lying down, stand gently to reduce the risk of dizziness or passing out.
The fundamental causes of hyperprolactinemia in women
Pituitary tumors, certain medications, polycystic ovarian syndrome (PCOS), hypothyroidism, or an unusual combination of hereditary factors may be responsible for the elevated prolactin levels of women. Your body functions similarly to a hormonal detective, albeit not in the manner of Sherlock Holmes.
Hyperprolactinemia diagnostic tests
In order to ascertain whether hyperprolactinemia is affecting your fertility, physicians may order blood tests to assess your prolactin levels or even brain imaging exams to identify any concealed lesions that are causing the disorder. It is redolent of an investigative program that is hormone-themed and features medical drama.
Effects of Hyperprolactinemia on Fertility Tests
The findings may be distorted when hyperprolactinemia disrupts your fertility tests, which can make it more challenging to identify the source of your reproductive issues. It is akin to endeavoring to complete a jigsaw puzzle with missing pieces: it is both frustrating and perplexing.
Medicines for hyperprolactinemia
Drugs such as dopamine agonists may be administered by physicians to assist in the reduction of prolactin levels to their normal state. They can be likened to bouncers, as they evict unwanted hormonal visitors that are causing turmoil in your body.
Lifestyle Change and Alternative Therapies
Lifestyle modifications, including stress reduction, sufficient sleep, and a nutritious diet, may be beneficial in maintaining healthy prolactin levels, in addition to medications. It is akin to hosting a tranquil pill party for your hormones; all are welcome, with the exception of those with an inordinate amount of prolactin.
The impact of hyperprolactinemia on menstrual irregularities
Menstrual abnormalities may result from elevated prolactin levels, which can disrupt the body’s natural hormonal equilibrium. Women with hyperprolactinemia may experience fluctuations in the frequency, duration, or severity of their menstrual cycles.
Relationship between Ovulation and Hyperprolactinemia
Fertility is contingent upon the discharge of eggs from the ovaries, which is known as ovulation. This process may be disrupted by hyperprolactinemia, which inhibits the production of hormones necessary for ovulation. This could potentially complicate the process of conception for women.
The Effect of Hyperprolactinemia on Male Reproductive Health
The prevalence of hyperprolactinemia is not restricted to women; it may also affect the fertility of men. Men with elevated prolactin levels may experience a decrease in testosterone production and sperm quality, which can have an impact on their fertility.
Treatment Options for Hyperprolactinemia in Men
Drugs that reduce prolactin levels are frequently employed to treat men’s hyperprolactinemia. Addressing this hormonal imbalance may improve the fertility and reproductive health of men.
Managing Hyperprolactinemia in Pregnancy and Postpartum
Hyperprolactinemia may result in premature labor or miscarriage during pregnancy. Healthcare professionals should conduct routine examinations of pregnant women with elevated prolactin levels to guarantee a healthy pregnancy.
Cabergoline is used to treat hyperprolactinemia (high levels of prolactin, a natural substance that helps breast-feeding women produce milk but can cause symptoms such as infertility, sexual problems, and bone loss in women who are not breast-feeding or men). Cabergoline is in a class of medications called dopamine receptor agonists. It works by decreasing the amount of prolactin in the body.
Postpartum hyperprolactinemia management
Some women may experience persistently elevated prolactin levels subsequent to childbirth, which may affect their menstrual cycles and milk supply. Treatment of hyperprolactinemia postpartum may involve the implementation of lifestyle modifications or the administration of medication to facilitate hormone regulation.
Dietary recommendations for hyperprolactinemia
Overall hormone health may be enhanced by consuming a diet that is nutrient-dense and well-balanced. Although additional research is necessary, certain studies indicate that foods like cereals, barley, and leafy greens may assist in the regulation of prolactin levels.
Hyperprolactinemia Complementary Therapies
In addition to conventional therapy, certain patients experience alleviation from hyperprolactinemia symptoms through alternative therapies, including yoga, acupuncture, or stress-reduction protocols. Standard therapy may be implemented in conjunction with these methodologies to facilitate hormonal equilibrium.
In conclusion, a comprehensive understanding of hyperprolactinemia and its treatment is necessary to effectively manage the disorder and its impact on fertility. By identifying the symptoms, receiving a prompt diagnosis, evaluating treatment options, and making essential lifestyle adjustments, individuals can empower themselves to successfully manage hyperprolactinemia and optimize their reproductive journey. Individuals who receive ongoing support from healthcare professionals and adopt a proactive management strategy may confidently navigate the obstacles presented by hyperprolactinemia in the hopes of achieving a positive outcome in their reproductive endeavors.